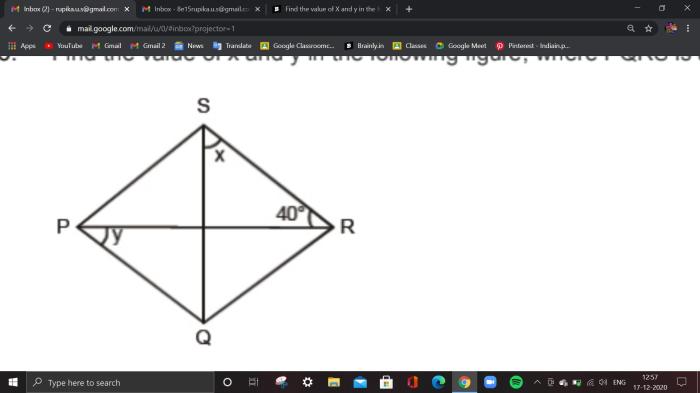
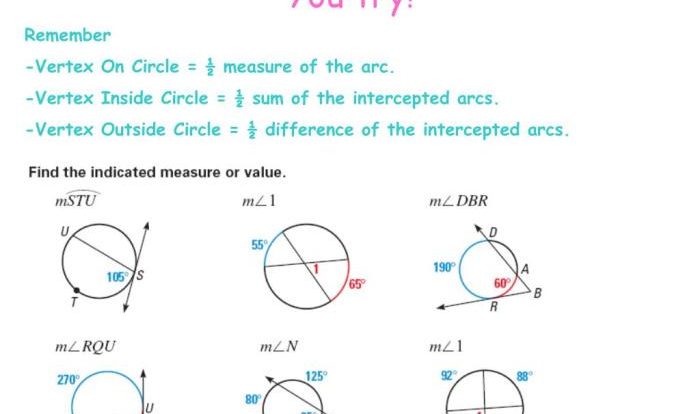
Angles of polygons scavenger hunt – Prepare for an exciting expedition into the world of angles of polygons! Join us on a scavenger hunt that will uncover the fascinating properties, measurements, and applications of these geometric shapes. Dive right in and let the angles guide your exploration.
From triangles to hexagons and beyond, we’ll unravel the relationship between the number of sides and angles in polygons. We’ll equip you with the tools and techniques to measure angles precisely, unlocking the secrets hidden within these shapes.
Polygon Angles
Polygons are closed plane figures with three or more straight sides and angles. The number of sides and angles in a polygon are related, with each side meeting at a vertex to form an angle.
The relationship between the number of sides and angles in a polygon can be expressed as: Number of angles = Number of sides.
Examples of Polygons
- Triangle: 3 sides, 3 angles
- Quadrilateral: 4 sides, 4 angles
- Pentagon: 5 sides, 5 angles
- Hexagon: 6 sides, 6 angles
- Octagon: 8 sides, 8 angles
Measuring Polygon Angles: Angles Of Polygons Scavenger Hunt
Measuring polygon angles is essential for understanding the properties and characteristics of polygons. Several tools and methods can be employed to accurately measure these angles, providing valuable insights into the geometric shapes.
Using a Protractor
A protractor is a common tool used to measure angles in polygons. It is a semi-circular device with a scale marked in degrees or radians. To measure an angle using a protractor, follow these steps:
- Place the center of the protractor on the vertex of the angle.
- Align the baseline of the protractor with one of the rays of the angle.
- Read the scale at the point where the other ray of the angle intersects the protractor.
By following these steps, you can accurately measure the angles of any polygon, providing a quantitative understanding of its geometric properties.
Properties of Polygon Angles
Polygons are two-dimensional shapes with straight sides. The angles formed by these sides have certain properties that are determined by the number of sides in the polygon.
Sum of Interior Angles, Angles of polygons scavenger hunt
The sum of the interior angles of a polygon with nsides is given by the formula:
(n
2) x 180 degrees
For example, a triangle ( n= 3) has a sum of interior angles of (3 – 2) x 180 = 180 degrees, while a pentagon ( n= 5) has a sum of interior angles of (5 – 2) x 180 = 540 degrees.
Exterior Angles
The exterior angle of a polygon is the angle formed by one side of the polygon and the extension of the adjacent side. The sum of the exterior angles of a polygon is always 360 degrees, regardless of the number of sides.
Relationship between Interior and Exterior Angles
The interior and exterior angles of a polygon are supplementary, meaning they add up to 180 degrees. This relationship can be used to find the measure of an exterior angle if the measure of the interior angle is known, and vice versa.
For example, if the interior angle of a polygon is 120 degrees, then the exterior angle is 180 – 120 = 60 degrees.
Applications of Polygon Angles
Polygon angles find extensive applications in various fields, including architecture, engineering, and design. They are crucial for understanding and calculating geometric properties, such as areas, volumes, and dimensions.
Architecture
In architecture, polygon angles play a vital role in determining the shape and structure of buildings. Architects use the angles of polygons to create aesthetically pleasing designs, optimize space utilization, and ensure structural stability.
- For example, the angles of a regular hexagon are used in the design of honeycombs, providing maximum strength and efficiency in nature.
- Similarly, the angles of a triangle are used in the construction of bridges and roofs, allowing for efficient load distribution and structural integrity.
Engineering
In engineering, polygon angles are used to design and analyze complex structures, such as bridges, machines, and aircraft. Engineers use the angles of polygons to calculate forces, stresses, and deformations.
- For example, the angles of a truss bridge are carefully designed to distribute weight evenly, ensuring the bridge’s stability under load.
- Similarly, the angles of a gear system are calculated to optimize the transmission of power and minimize friction.
Design
In design, polygon angles are used to create visually appealing and functional products. Designers use the angles of polygons to create patterns, logos, and even entire products.
- For example, the angles of a hexagon are used in the design of soccer balls, providing a uniform and aerodynamic shape.
- Similarly, the angles of a pentagon are used in the design of star-shaped logos, creating a visually striking and memorable image.
Detailed FAQs
What is a polygon?
A polygon is a closed, two-dimensional shape with straight sides.
How do you measure the angles of a polygon?
You can use a protractor to measure the angles of a polygon by placing the protractor’s center point on the vertex of the angle and aligning its baseline with one of the sides of the angle.
What is the sum of the interior angles of a polygon with n sides?
(n – 2) x 180 degrees