Activity 9.5 relief and gradient slope analysis – Activity 9.5: Relief and Gradient Slope Analysis stands as a pivotal investigation in the realm of geographic studies, offering profound insights into the intricate characteristics of landscapes. This analysis unveils the significance of relief and gradient slope, providing a comprehensive understanding of terrain variations and their impact on various natural processes.
Through meticulous data collection, processing, and interpretation, this analysis empowers researchers to unravel the complexities of landforms, unlocking a wealth of information that aids in comprehending the Earth’s dynamic systems.
Activity 9.5: Relief and Gradient Slope Analysis

Activity 9.5 focuses on analyzing relief and gradient slope, two fundamental geographic characteristics that play a crucial role in understanding the physical landscape and its implications for various processes.
The activity involves collecting data on elevation and slope, processing and preparing it for analysis, and applying appropriate techniques to derive insights about the terrain’s morphology and potential implications for erosion, landform development, and human activities.
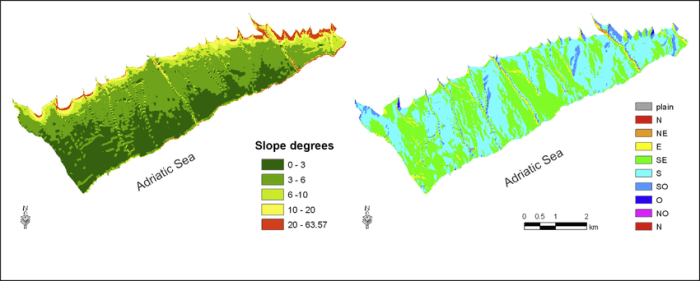
Relief and Gradient Slope Analysis
Relief refers to the vertical variation in the elevation of a landscape, while gradient slope represents the steepness of the terrain. Analyzing these characteristics provides valuable information about the geomorphology of an area, its susceptibility to erosion, and its potential for land use and development.
Data Collection and Processing
Data for relief and gradient slope analysis can be collected using various methods, including topographic maps, aerial photographs, and digital elevation models (DEMs). These data sources provide information about the elevation and slope of the terrain, which is then processed and prepared for analysis.
Data processing typically involves converting the elevation data into a digital format, correcting for errors and artifacts, and interpolating data points to create a continuous surface representing the terrain.
Analysis Techniques
Numerous techniques are employed to analyze relief and gradient slope data. These techniques include:
- Hypsometric analysis: Examines the distribution of elevation values within a landscape.
- Slope analysis: Calculates the steepness of the terrain at each point and identifies areas with high or low slopes.
- Landform classification: Categorizes landforms based on their relief and slope characteristics.
Interpretation and Application, Activity 9.5 relief and gradient slope analysis
The results of relief and gradient slope analysis can be interpreted to provide insights about the landscape’s evolution, its susceptibility to erosion, and its potential for various land uses.
Applications of this analysis include:
- Geomorphology: Understanding the processes that shape the landscape.
- Geology: Identifying geological structures and formations.
- Environmental science: Assessing erosion potential and water flow patterns.
FAQ Overview: Activity 9.5 Relief And Gradient Slope Analysis
What is the primary objective of Activity 9.5: Relief and Gradient Slope Analysis?
The primary objective of Activity 9.5 is to provide a comprehensive understanding of the significance of relief and gradient slope in geographic studies, enabling researchers to analyze and interpret terrain variations.
What methods are employed to collect data for this analysis?
Data collection methods for relief and gradient slope analysis include topographic maps, aerial photographs, satellite imagery, and field surveys.
How are the results of this analysis interpreted?
The results of relief and gradient slope analysis are interpreted by examining the patterns and relationships between relief and slope data, which provide insights into landform evolution, erosion processes, and other geomorphic phenomena.