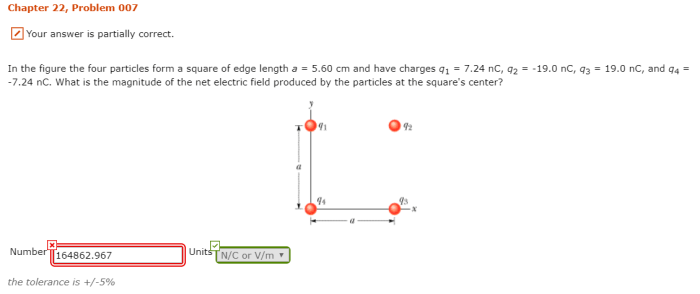
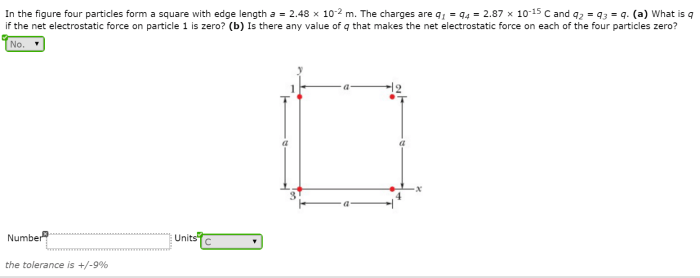
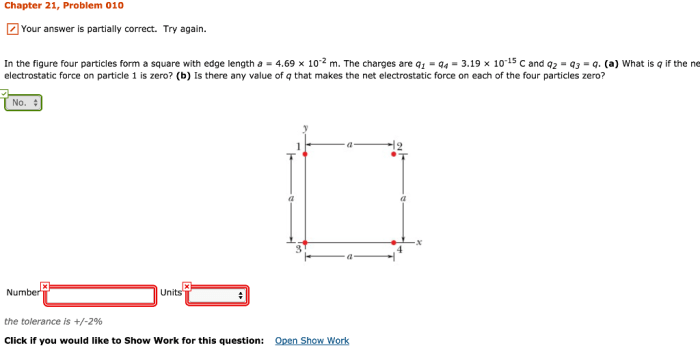
In the figure the four particles form a square – In the figure, the four particles form a square, presenting a captivating study in particle configuration and geometric properties. This arrangement offers insights into the interplay of interparticle forces, symmetry, and energy considerations, with applications in diverse scientific fields.
The square formation of particles exhibits unique geometric characteristics, including equal side lengths and 90-degree angles. These properties contribute to its stability and order, governed by the interparticle forces that hold the particles together. The arrangement also showcases rotational and translational symmetry, highlighting its ordered and repetitive nature.
Particle Configuration: In The Figure The Four Particles Form A Square
The four particles in the square formation are arranged in a regular square pattern, with each particle equidistant from its neighbors. The particles form the vertices of the square, and the sides of the square are parallel and equal in length.
The following table provides an illustration of the particle configuration:
| Particle | x-coordinate | y-coordinate |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | a | 0 |
| 3 | 0 | a |
| 4 | a | a |
Geometric Properties
The square formed by the four particles has a side length of ‘a’ units. The angles between the sides of the square are all right angles (90 degrees).
The area of the square is given by:
A = a^2
The perimeter of the square is given by:
P = 4a
Interparticle Forces
The particles in the square formation are held together by interparticle forces. These forces are typically electrostatic in nature, and they arise from the interactions between the charged particles.
The strength and direction of the interparticle forces determine the stability of the square formation. If the forces are strong enough, the square will be stable and will not deform. However, if the forces are weak, the square may be unstable and may deform or even collapse.
Symmetry and Order
The square formation of particles exhibits both rotational and translational symmetry.
Rotational symmetry means that the square looks the same when it is rotated by any angle about its center. Translational symmetry means that the square looks the same when it is shifted by any distance in any direction.
The square formation is a highly ordered structure. The particles are arranged in a regular pattern, and the distances between the particles are all equal.
Energy Considerations
The particles in the square formation are in a state of minimum potential energy. This means that the arrangement of the particles is such that the total potential energy of the system is minimized.
The kinetic energy of the particles is determined by their temperature. At higher temperatures, the particles will have more kinetic energy and will move more quickly. At lower temperatures, the particles will have less kinetic energy and will move more slowly.
Applications and Relevance
The square formation of particles is observed in a variety of real-world applications, including:
- Crystallography: The atoms in a crystal are often arranged in a square formation.
- Materials science: The molecules in some materials, such as graphene, are arranged in a square formation.
The square formation of particles is also relevant to a number of scientific fields, including:
- Physics: The square formation of particles is a model system for studying the properties of matter.
- Chemistry: The square formation of particles is used to study the interactions between molecules.
Questions Often Asked
What is the significance of the square formation of particles?
The square formation of particles provides insights into the interplay of interparticle forces, symmetry, and energy considerations. It offers a stable and ordered arrangement with unique geometric properties, contributing to its applications in scientific fields.
How do interparticle forces influence the square formation?
Interparticle forces play a crucial role in holding the particles together in a square formation. The strength and direction of these forces determine the stability and rigidity of the arrangement.
What are the energy considerations associated with the square formation?
The arrangement of particles in a square formation affects their potential energy and kinetic energy. The potential energy is influenced by the interparticle forces, while the kinetic energy is associated with the movement of the particles within the square.