Review sheet 38 anatomy of the digestive system – Delving into the intricate world of the human body, we present Review Sheet 38: Anatomy of the Digestive System. This comprehensive guide embarks on an exploration of the organs, structures, and processes involved in the essential function of nutrient absorption and waste elimination.
From the initial ingestion of food to its final expulsion, we meticulously dissect each stage of the digestive journey, unraveling the complexities of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and accessory organs. Prepare to be captivated as we illuminate the microscopic anatomy and clinical applications associated with this vital system.
1. Digestive System Overview
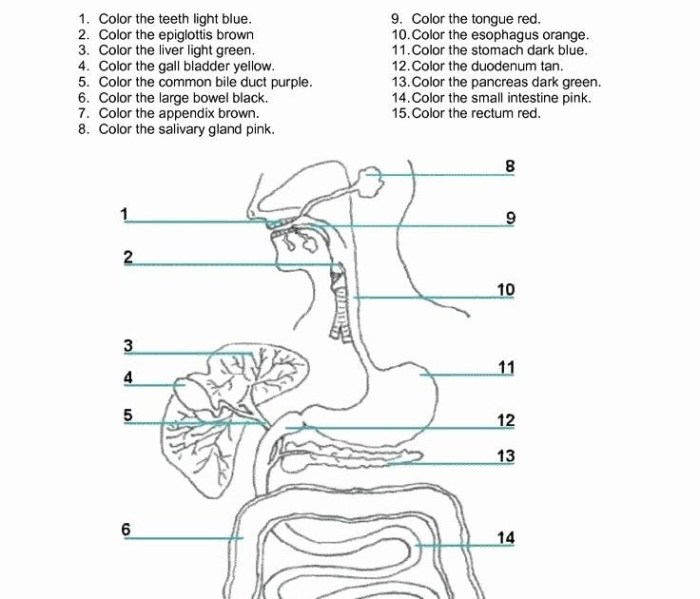
The digestive system is a complex network of organs that work together to break down food, absorb nutrients, and eliminate waste. The primary function of the digestive system is to provide the body with the energy and nutrients it needs to function properly.
The major organs involved in the digestive process include the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, pancreas, and liver. Each organ plays a specific role in breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and eliminating waste.
The overall process of digestion begins with ingestion, which is the process of taking food into the mouth. The food is then chewed and mixed with saliva, which helps to break it down into smaller pieces. The food is then swallowed and travels down the esophagus into the stomach.
2. Anatomy of the Mouth and Esophagus: Review Sheet 38 Anatomy Of The Digestive System
The mouth is the first part of the digestive system. It is lined with teeth, which help to break down food into smaller pieces. The mouth also contains the tongue, which helps to move food around and mix it with saliva.
The esophagus is a muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach. The esophagus uses peristalsis, a series of involuntary muscle contractions, to move food down into the stomach.
Swallowing is a complex process that involves the coordinated action of the mouth, tongue, and esophagus. When you swallow, the tongue pushes the food back into the throat, which triggers the epiglottis to close off the airway. The food then travels down the esophagus into the stomach.
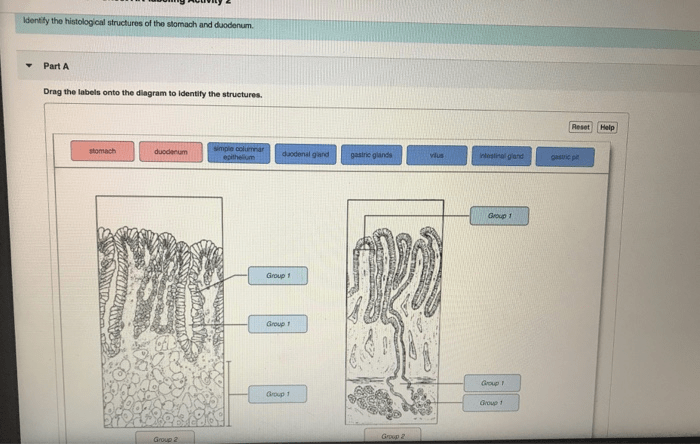
3. Anatomy of the Stomach
The stomach is a J-shaped organ that is located on the left side of the abdomen. The stomach is responsible for storing food and breaking it down into smaller pieces. The stomach also produces gastric juices, which contain hydrochloric acid and enzymes that help to break down food.
The stomach is divided into three regions: the fundus, the body, and the antrum. The fundus is the upper region of the stomach and it stores food. The body is the middle region of the stomach and it breaks down food into smaller pieces.
The antrum is the lower region of the stomach and it empties food into the small intestine.
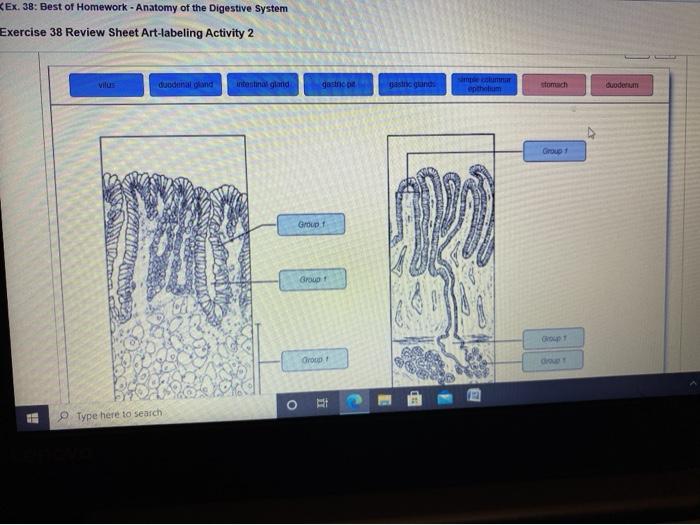
4. Anatomy of the Small Intestine
The small intestine is a long, coiled tube that is located in the abdomen. The small intestine is responsible for absorbing nutrients from food. The small intestine is divided into three sections: the duodenum, the jejunum, and the ileum.
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine and it receives food from the stomach. The duodenum is also where bile and pancreatic juices are added to food. Bile helps to break down fats, and pancreatic juices contain enzymes that help to break down proteins and carbohydrates.
The jejunum is the middle section of the small intestine and it is responsible for absorbing nutrients from food. The jejunum is lined with villi, which are small, finger-like projections that increase the surface area for absorption.
The ileum is the last section of the small intestine and it is responsible for absorbing water and electrolytes from food. The ileum is also where bacteria are found. These bacteria help to break down food and produce vitamins.
General Inquiries
What is the primary function of the digestive system?
The primary function of the digestive system is to break down ingested food into absorbable nutrients and eliminate waste products.
What are the major organs involved in the digestive process?
The major organs involved in the digestive process include the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, pancreas, and liver.
What is the role of gastric juices in digestion?
Gastric juices, produced by the stomach, contain hydrochloric acid and enzymes that aid in the breakdown of proteins and initiate the digestive process.