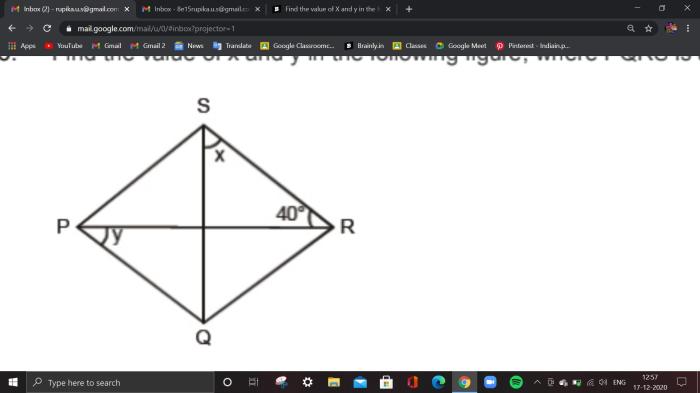
Embark on an intellectual journey with our comprehensive secants tangents and angles assignment, meticulously crafted to illuminate the intricate world of geometry. This assignment will empower you with a profound understanding of secants, tangents, and their captivating relationships with circles, angles, and trigonometric functions.
Prepare to delve into the fascinating realm of geometry, where lines intersect circles, angles unfold, and trigonometric identities take shape. Our meticulously designed assignment will guide you through the intricacies of secants and tangents, unlocking their secrets and revealing their practical applications in the world around us.
Secants and Tangents Definitions
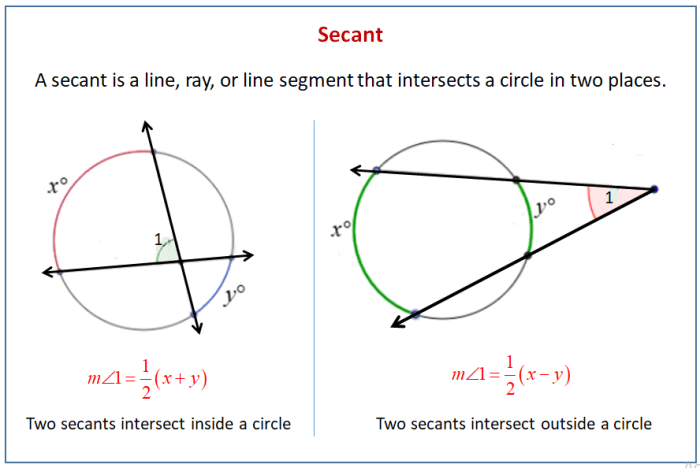
In geometry, a secant is a line that intersects a circle at two distinct points. A tangent is a line that touches a circle at exactly one point.
Visual Representations of Secants and Tangents
Here are some visual representations of secants and tangents:
- Secant:
- Tangent:
Relationships Between Secants, Tangents, and Circles
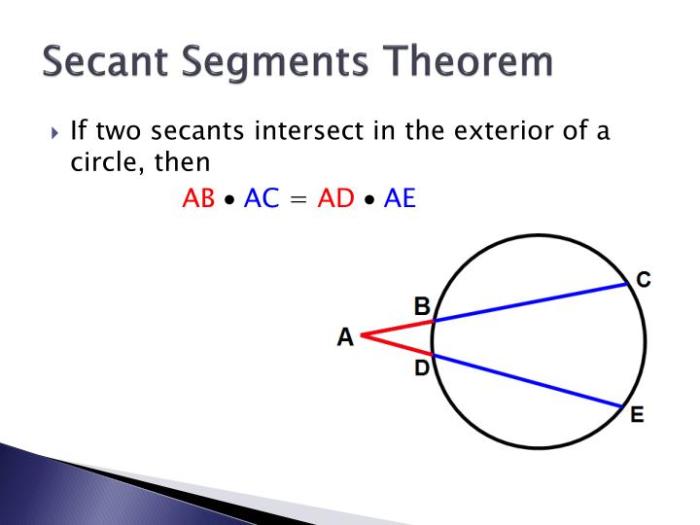
How Secants Intersect Circles
When a secant intersects a circle, it creates two arcs. The measure of each arc is equal to half the measure of the central angle that intercepts the arc.
How Tangents Touch Circles
When a tangent touches a circle, it is perpendicular to the radius drawn to the point of tangency. The radius and the tangent form a right angle.
Examples of Secants and Tangents Drawn on a Circle
Here are some examples of secants and tangents drawn on a circle:
- Secant: A line that passes through the center of the circle and intersects the circle at two other points.
- Tangent: A line that touches the circle at exactly one point.
Angles Formed by Secants and Tangents
How to Measure the Angle Formed by Two Secants, Secants tangents and angles assignment
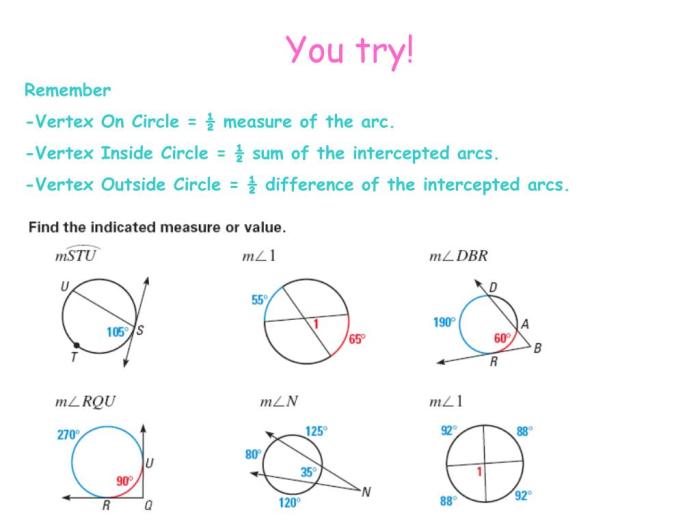
To measure the angle formed by two secants, draw a radius from the center of the circle to the point of intersection of the secants. The angle formed by the two secants is equal to half the sum of the measures of the intercepted arcs.
How to Measure the Angle Formed by a Secant and a Tangent
To measure the angle formed by a secant and a tangent, draw a radius from the center of the circle to the point of tangency. The angle formed by the secant and the tangent is equal to half the measure of the intercepted arc.
Relationship Between the Angles Formed by Secants and Tangents
The angles formed by secants and tangents are related by the following theorem: The angle formed by two secants is equal to the sum of the angles formed by the secants and the tangents.
Applications of Secants and Tangents
How Secants and Tangents Are Used in Geometry
Secants and tangents are used in geometry to solve a variety of problems, such as finding the length of a chord, finding the measure of an angle, and constructing circles.
Examples of Real-World Applications of Secants and Tangents
Secants and tangents have a variety of real-world applications, such as:
- Navigation: Secants and tangents are used to calculate the distance between two points on a sphere, such as the Earth.
- Engineering: Secants and tangents are used to design bridges, buildings, and other structures.
- Architecture: Secants and tangents are used to design curves and arches in buildings.
Secants, Tangents, and Trigonometry: Secants Tangents And Angles Assignment
How Secants and Tangents Are Related to Trigonometric Functions
Secants and tangents are related to the trigonometric functions sine, cosine, and tangent. The secant of an angle is equal to the reciprocal of the cosine of the angle, and the tangent of an angle is equal to the ratio of the sine of the angle to the cosine of the angle.
Formulas That Involve Secants and Tangents
Here are some formulas that involve secants and tangents:
- sec(θ) = 1/cos(θ)
- tan(θ) = sin(θ)/cos(θ)
Table Comparing the Trigonometric Functions of Secants and Tangents
Here is a table comparing the trigonometric functions of secants and tangents:
| Function | Secant | Tangent |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | 1/cos(θ) | sin(θ)/cos(θ) |
| Range | [-1, ∞) | (-∞, ∞) |
| Period | 2π | π |
Essential Questionnaire
What is the key difference between a secant and a tangent?
A secant intersects a circle at two distinct points, while a tangent touches a circle at only one point.
How do you calculate the length of a tangent from a secant?
The length of a tangent from a secant can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem or trigonometric ratios.
What is the relationship between the angle formed by two secants and the angle formed by the tangents drawn at the points of intersection?
The angle formed by two secants is equal to half the sum of the angles formed by the tangents drawn at the points of intersection.