Unlabeled diagram of animal cell – Embarking on an exploration of the unlabeled diagram of an animal cell, we delve into a captivating realm of biological intricacies. This enigmatic representation holds the key to understanding the fundamental building blocks of life, offering a window into the inner workings of these microscopic marvels.
Within this comprehensive guide, we will unravel the structure and function of an animal cell, deciphering the roles of its various organelles and examining how they orchestrate a symphony of cellular processes. Prepare to be enthralled as we unveil the secrets of the unlabeled animal cell, shedding light on its essential role in the intricate tapestry of life.
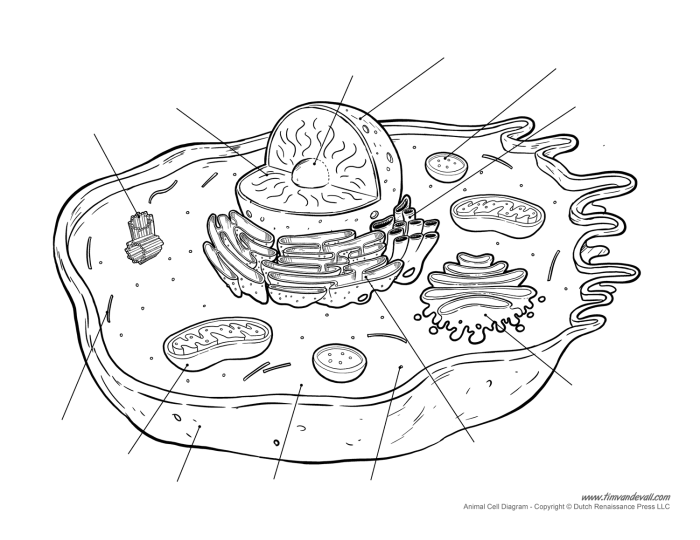
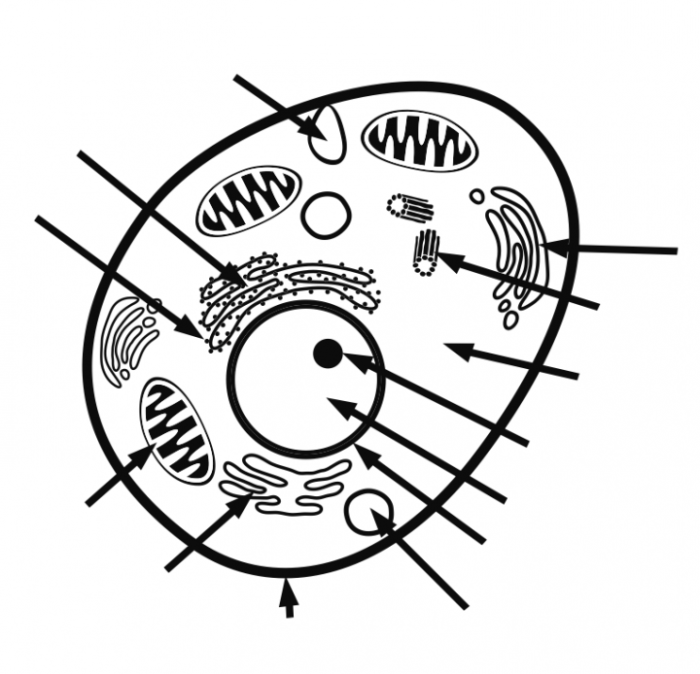
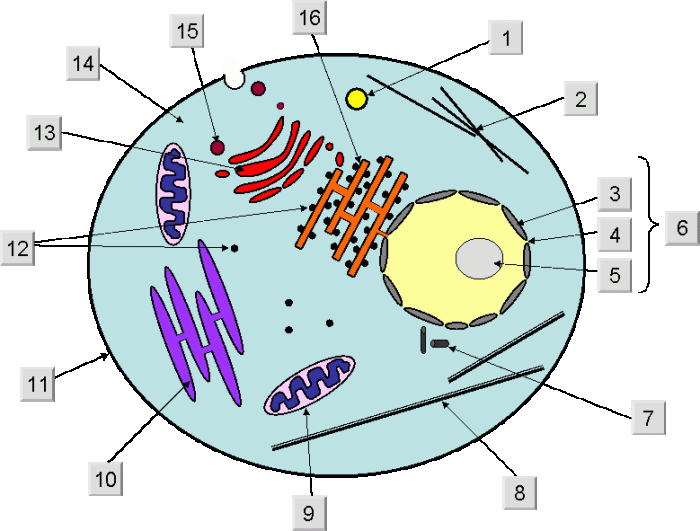
Unlabeled Diagram of Animal Cell
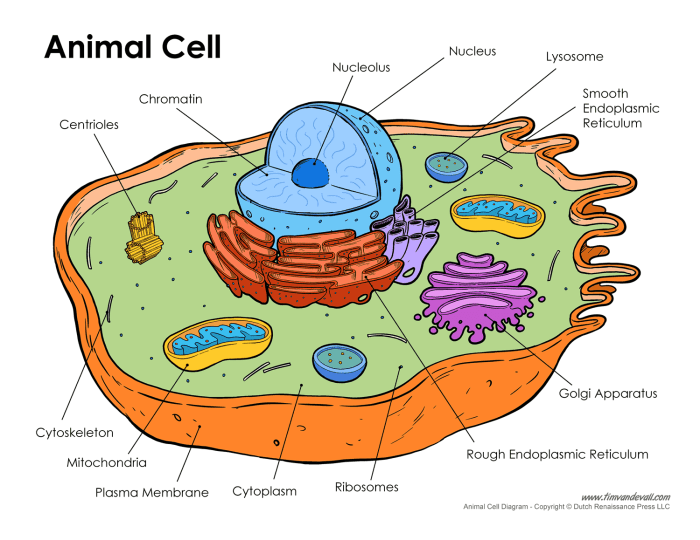
Animal cells are the basic unit of life for animals. They are composed of a variety of organelles, each with its own specific function. The cell membrane surrounds the cell and protects its contents. The cytoplasm is a gel-like substance that fills the cell and contains the organelles.
The nucleus is the control center of the cell and contains the cell’s DNA. The mitochondria are responsible for producing energy for the cell. The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes that folds and transports proteins. The Golgi apparatus is a stack of membranes that modifies and packages proteins.
The lysosomes are small sacs that contain digestive enzymes. The peroxisomes are small sacs that contain enzymes that break down toxic substances. The vacuoles are small sacs that store food and water. The ribosomes are small particles that synthesize proteins.
The cytosol is the fluid that fills the cell and contains all of the cell’s organelles.
Cell Organelles, Unlabeled diagram of animal cell
- Nucleus:The nucleus is the control center of the cell and contains the cell’s DNA.
- Cytoplasm:The cytoplasm is a gel-like substance that fills the cell and contains the organelles.
- Cell membrane:The cell membrane surrounds the cell and protects its contents.
- Mitochondria:The mitochondria are responsible for producing energy for the cell.
- Endoplasmic reticulum:The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes that folds and transports proteins.
- Golgi apparatus:The Golgi apparatus is a stack of membranes that modifies and packages proteins.
- Lysosomes:The lysosomes are small sacs that contain digestive enzymes.
- Peroxisomes:The peroxisomes are small sacs that contain enzymes that break down toxic substances.
- Vacuoles:The vacuoles are small sacs that store food and water.
- Ribosomes:The ribosomes are small particles that synthesize proteins.
- Cytosol:The cytosol is the fluid that fills the cell and contains all of the cell’s organelles.
Cell Division
Cell division is the process by which a cell divides into two new cells. There are two types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis is the process by which a cell divides into two identical daughter cells. Meiosis is the process by which a cell divides into four haploid daughter cells.
Animal Cell vs. Plant Cell
- Cell wall:Plant cells have a cell wall, while animal cells do not.
- Chloroplasts:Plant cells have chloroplasts, while animal cells do not.
- Vacuoles:Plant cells have a large central vacuole, while animal cells have many small vacuoles.
Helpful Answers
What is the purpose of an unlabeled diagram of an animal cell?
An unlabeled diagram of an animal cell provides a visual representation of the cell’s structure, allowing students and researchers to identify and understand the functions of its various organelles without the distraction of labels.
How can I use an unlabeled diagram of an animal cell in my teaching?
Unlabeled diagrams are a valuable tool for engaging students and assessing their understanding of cell structure. By providing them with an unlabeled diagram, you can encourage them to actively engage with the material and test their knowledge of the different organelles.
Where can I find high-quality unlabeled diagrams of animal cells?
Numerous online resources provide access to high-quality unlabeled diagrams of animal cells. These resources include educational websites, scientific databases, and textbooks.