Lesson 9.1 the anatomy of the lungs – Embarking on Lesson 9.1: The Anatomy of the Lungs, we embark on an enlightening journey into the intricate structure and function of these vital organs. This exploration unveils the complexities of the respiratory system, shedding light on the mechanisms that sustain life.
Within the thoracic cavity, the lungs reside as a pair of asymmetrical structures, each divided into distinct lobes. The pleura, a protective membrane, envelops the lungs, safeguarding them from external influences. Delving deeper, we encounter the bronchial tree, a network of airways that facilitate the exchange of gases.
1. Introduction
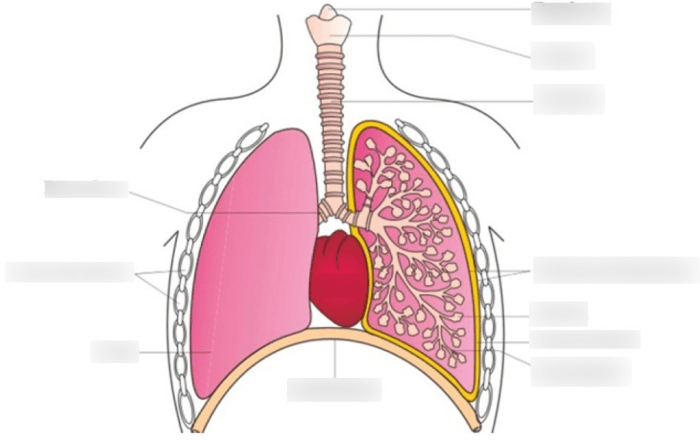
This lesson delves into the anatomy of the lungs, providing a comprehensive understanding of their structure and function. The respiratory system, consisting of the lungs and airways, is essential for gas exchange, maintaining homeostasis, and overall well-being.
2. Gross Anatomy of the Lungs
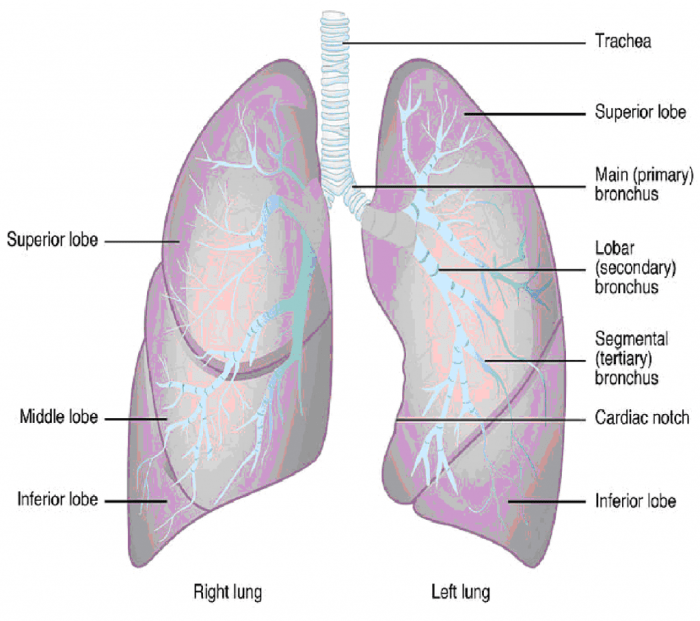
Location and Shape
The lungs are located within the thoracic cavity, protected by the rib cage. They are cone-shaped organs, with the apex extending superiorly and the base resting on the diaphragm inferiorly.
Differences Between Right and Left Lungs
- Right lung:Consists of three lobes (upper, middle, and lower) separated by two fissures (oblique and horizontal).
- Left lung:Has two lobes (upper and lower) divided by an oblique fissure.
Pleura
The pleura is a serous membrane that lines the thoracic cavity and covers the lungs. It consists of two layers: the visceral pleura (adhering to the lung surface) and the parietal pleura (lining the thoracic cavity).
3. Internal Anatomy of the Lungs: Lesson 9.1 The Anatomy Of The Lungs
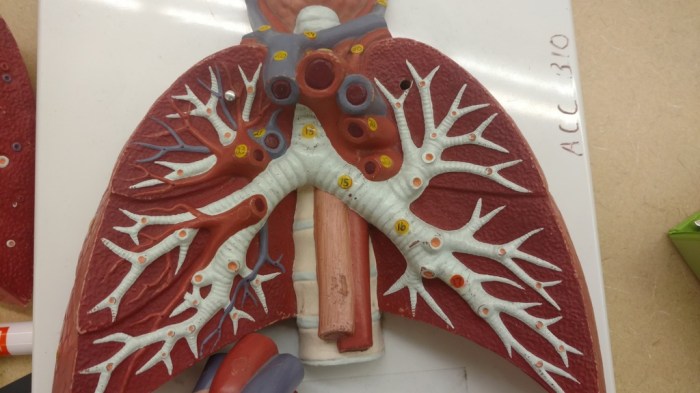
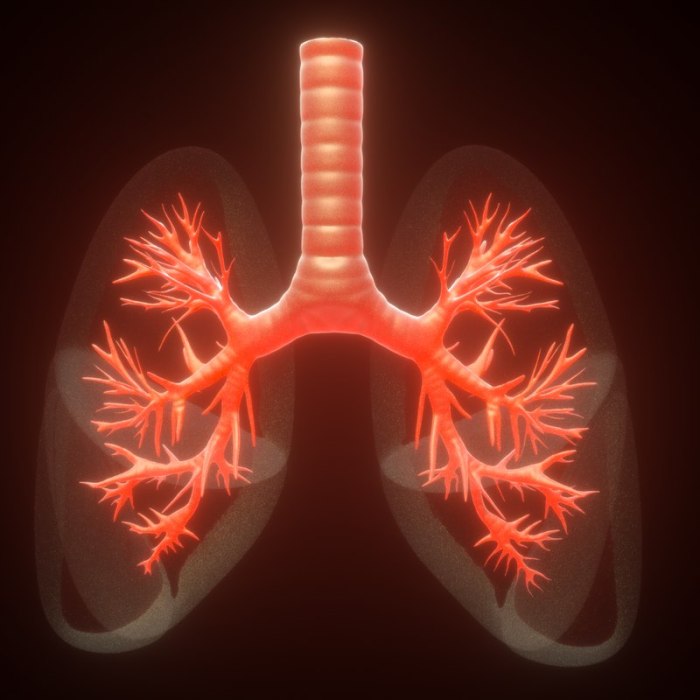
Bronchial Tree
The bronchial tree is a system of branching airways that conduct air to and from the lungs. It consists of the trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles.
Alveoli, Lesson 9.1 the anatomy of the lungs
Alveoli are tiny air sacs where gas exchange occurs. They have a thin, delicate structure, maximizing the surface area for oxygen and carbon dioxide diffusion.
Pulmonary Circulation
The pulmonary circulation involves the flow of blood between the heart and the lungs. It carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs for oxygenation and returns oxygenated blood to the heart.
4. Histology of the Lungs
Cellular Components
- Type I pneumocytes:Thin, squamous cells that facilitate gas exchange.
- Type II pneumocytes:Cuboidal cells that secrete pulmonary surfactant.
- Macrophages:Phagocytic cells that remove debris and pathogens.
- Fibroblasts:Cells that produce collagen and other extracellular matrix components.
Extracellular Matrix
The extracellular matrix provides structural support and elasticity to the lungs. It consists of collagen, elastin, and proteoglycans.
Pulmonary Surfactant
Pulmonary surfactant is a lipoprotein complex that reduces surface tension in the alveoli, preventing their collapse.
5. Clinical Applications
Respiratory Diseases
- Asthma:Chronic inflammatory disease causing airway narrowing and bronchospasm.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD):Progressive lung disease characterized by airflow limitation.
- Pneumonia:Infection of the lung parenchyma, causing inflammation and fluid accumulation.
Imaging Techniques
- Chest X-rays:Provide a general overview of the lungs and detect abnormalities such as pneumonia or lung tumors.
- CT scans:Cross-sectional imaging that offers detailed views of the lungs, aiding in diagnosing conditions like emphysema or lung cancer.
Pulmonary Function Testing
Pulmonary function tests assess lung function by measuring parameters such as lung volumes, capacities, and flow rates. They help diagnose and monitor respiratory disorders.
Top FAQs
What is the primary function of the lungs?
The lungs facilitate gas exchange, enabling the uptake of oxygen and the release of carbon dioxide.
Describe the structure of the bronchial tree.
The bronchial tree consists of the trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles, which form a branching network of airways.
What is the role of the alveoli in respiration?
Alveoli are tiny air sacs where gas exchange occurs between the lungs and the bloodstream.