Welcome to the ultimate guide to Chapter 10 Test A Geometry Answers! This resource has been meticulously crafted to provide you with a thorough understanding of the key concepts and problem-solving strategies covered in this chapter. Whether you’re a student looking to ace your test or an educator seeking to enhance your teaching, this guide has everything you need.
Throughout this guide, we’ll explore the fundamental concepts of geometry, including angles, triangles, and circles. We’ll also delve into effective problem-solving strategies, such as using geometric properties and theorems to tackle complex problems. Along the way, we’ll provide plenty of practice problems and detailed solutions to reinforce your understanding.
Key Concepts and Definitions
Chapter 10 of geometry introduces foundational concepts that form the basis for understanding more advanced geometric principles. These concepts include angles, triangles, and circles, each with its own unique properties and characteristics.
An angleis formed by two rays that share a common endpoint, known as the vertex. Angles are measured in degrees, with a full rotation measuring 360 degrees.
A triangleis a polygon with three sides and three angles. Triangles are classified based on the lengths of their sides (scalene, isosceles, equilateral) and the measures of their angles (acute, right, obtuse).
A circleis a plane figure consisting of all points equidistant from a fixed point called the center. Circles are characterized by their radius, which is the distance from the center to any point on the circle, and their circumference, which is the distance around the circle.
Problem-Solving Strategies
Geometry problems often require a systematic approach to find solutions. Effective problem-solving strategies involve understanding the problem, drawing diagrams, identifying relevant properties and theorems, and applying logical reasoning.
Angle and Triangle Problems
- Draw diagrams:Visualizing the problem with a diagram helps identify angles and relationships.
- Use angle properties:Sum of interior angles of a triangle is 180 degrees, exterior angle equals the sum of the opposite interior angles.
- Apply triangle congruence theorems:SAS, SSS, ASA, AAS, and HL can be used to prove triangles congruent and find unknown angles.
Complex Geometry Problems, Chapter 10 test a geometry answers
- Break down the problem:Divide the problem into smaller, manageable parts.
- Use geometric properties:Apply properties such as the Pythagorean theorem, distance formula, and area formulas.
- Construct proofs:Use deductive reasoning and logical arguments to prove statements and solve problems.
Types of Geometry Problems
Geometry problems in Chapter 10 can be categorized into various types, each requiring specific strategies and concepts for solving. Understanding these types is crucial for efficient problem-solving and concept application.
Angle Measurement
Problems involving angles focus on determining the measures of angles formed by intersecting lines or within geometric figures. These problems require knowledge of angle properties, angle relationships (e.g., supplementary, complementary), and angle bisectors.
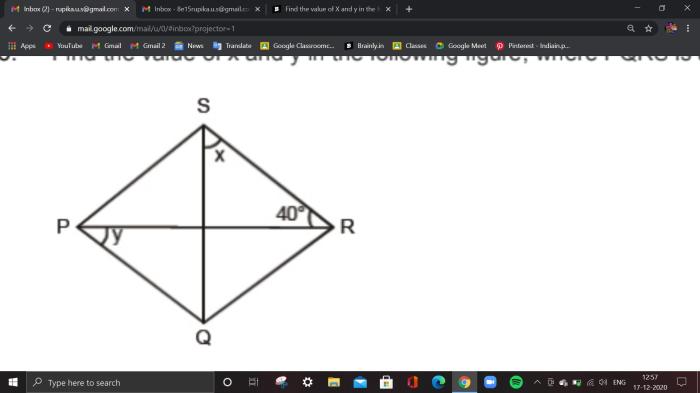
- Find the measure of an angle formed by two intersecting lines.
- Determine the sum of angles in a triangle or quadrilateral.
- Calculate the angle of depression or elevation.
Triangle Classification
Triangle classification problems involve determining the type of triangle based on its side lengths or angle measures. This requires an understanding of triangle properties, such as side and angle relationships, as well as the Pythagorean theorem.
- Classify a triangle as equilateral, isosceles, or scalene.
- Determine whether a triangle is right, acute, or obtuse.
- Find the side lengths of a triangle given its type.
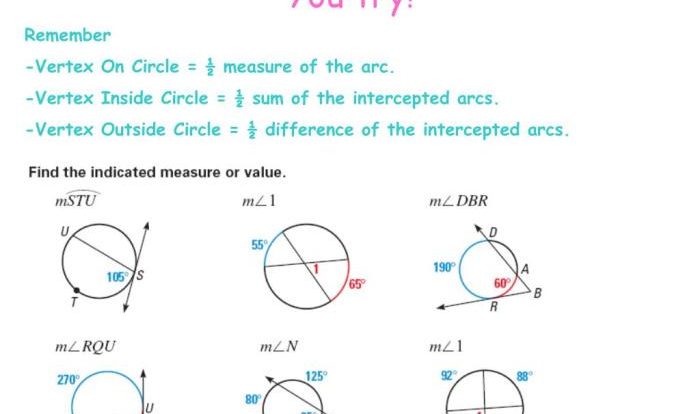
Circle Properties
Circle property problems focus on applying the properties of circles to solve problems related to their circumferences, areas, radii, and chords. These problems require knowledge of circle definitions, formulas, and relationships.
- Calculate the circumference or area of a circle given its radius.
- Find the length of a chord or the measure of an inscribed angle.
- Determine the center of a circle given three points on its circumference.
Applications of Geometry
Geometry, a branch of mathematics concerned with the properties of shapes, has a wide range of practical applications in real-world scenarios. From designing buildings and bridges to creating artwork and understanding the natural world, geometry plays a crucial role in various fields and aspects of everyday life.
In the field of architecture, geometry is essential for designing and constructing buildings. Architects use geometric principles to create structures that are both aesthetically pleasing and structurally sound. They consider factors such as shape, symmetry, and proportion to ensure the stability and functionality of buildings.
Engineering
In engineering, geometry is applied in various disciplines, including civil, mechanical, and electrical engineering. Civil engineers use geometry to design and build infrastructure projects such as roads, bridges, and dams. Mechanical engineers apply geometric principles in designing and manufacturing machines, vehicles, and other mechanical systems.
Electrical engineers utilize geometry in the design and analysis of electrical circuits and systems.
Design
Geometry also plays a significant role in the field of design, including graphic design, interior design, and industrial design. Graphic designers use geometric shapes and patterns to create visually appealing designs for logos, websites, and other graphic materials. Interior designers apply geometric principles to create functional and aesthetically pleasing interior spaces.
Industrial designers use geometry to design products that are both visually appealing and ergonomically sound.
Everyday Life
Geometry is not limited to professional fields; it also has practical applications in everyday life. For example, understanding geometry can help us navigate our surroundings, estimate distances, and solve spatial puzzles. It is also essential in activities such as woodworking, gardening, and cooking.
Practice Problems and Solutions
In this section, we will provide a collection of practice problems that cover the key concepts of Chapter 10. Each problem is accompanied by a detailed step-by-step solution to help you understand the problem-solving process.
Problem Types
The practice problems will cover a variety of problem types, including:
- Finding the area and perimeter of polygons
- Solving for unknown side lengths or angles
- Applying geometric formulas to real-world problems
Table of Problems and Solutions
The following table presents the practice problems and their solutions:
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Find the area of a rectangle with a length of 5 cm and a width of 3 cm. | The area of a rectangle is given by the formula A = l
|
| Find the perimeter of a square with a side length of 4 cm. | The perimeter of a square is given by the formula P = 4
|
| Find the length of the diagonal of a square with a side length of 5 cm. | The length of the diagonal of a square is given by the formula d = s
|
| Find the area of a triangle with a base of 6 cm and a height of 4 cm. | The area of a triangle is given by the formula A = 1/2
|
| Find the volume of a cube with a side length of 3 cm. | The volume of a cube is given by the formula V = s3, where s is the length of a side. Substituting the given value, we get V = 3 cm3 = 27 cm3. |
Question & Answer Hub: Chapter 10 Test A Geometry Answers
What are the key concepts covered in Chapter 10 Test A Geometry?
Chapter 10 Test A Geometry covers the fundamental concepts of geometry, including angles, triangles, and circles. We’ll explore their properties, relationships, and how to solve problems involving them.
What are some effective problem-solving strategies for geometry problems?
Effective problem-solving strategies for geometry problems include using geometric properties and theorems, breaking down complex problems into smaller steps, and drawing diagrams to visualize the problem.
How can I practice solving geometry problems?
Practice is key to mastering geometry. This guide provides numerous practice problems with detailed solutions to help you reinforce your understanding. Additionally, you can find practice problems in your textbook or online resources.